Procurement Cycle: 17 Steps to an Ideal Procurement Process

In a globalized world, many businesses have realized that the right procurement strategy is an indispensable business catalyst. They are becoming increasingly aware of its incredible impact on an organization’s bottom line and strategic business operations. But amidst all this alacrity, a gnawing misconception making the round is that establishing a structured and tactical procurement process is unattainable.
You must have heard or read this statement often- Procurement is a complex web of overlapping functions. It comprises multiple workflows such as market analysis, supplier selection, issuing RPFs/ RFQs, and negotiating contracts, making many procurement managers scowl. Not to forget, the mounting pressure of tight timelines and living up to customer expectations makes the task extremely challenging. Now, amidst all this, when businesses don’t follow a proper structure and undertake a short-sighted approach to the procurement process, it can hurt the company, fueling the apprehension mentioned above.
Fortunately, we are here to dispel the myths holding you back from setting up an ideal procurement cycle that can poise your business for success. In this blog, we will define procurement. What do we mean by a perfect procurement cycle? Why is it integral for procurement managers to know the procurement process in detail? How can businesses optimize their stages of the procurement process with technology?
What is procurement?
Procurement refers to a series of activities or processes involved in acquiring goods and services essential for a business to operate. It starts with identifying needs, specifying requirements, conducting market research, evaluating suppliers, and negotiating contracts, and ends with monitoring and managing supplier relationships. Procurement is a critical component in business as it enhances spending transparency and capitalizes on steady movements in the supply chain.
An optimized procurement process can help organizations manage supply chain risks. By this, we don’t mean purchasing goods or services; instead, we suggest ensuring process efficiency at every stage of the procurement cycle with proper management of the supply chain.
What is a procurement cycle?
The procurement lifecycle refers to activities undertaken to purchase goods and services. Conducted in a proper sequence, the procurement cycle entails a sequence of comprehensive processes that begin when you first interact with your potential suppliers and end when your organization has procured the required items for the production team. An efficient procurement process reduces costs and improves operational flows.
What are the stages of a procurement process?
Properly segmenting the procurement lifecycle helps businesses scale better with high growth and revenue. It supports identifying inefficiencies, reducing delivery times, and finding quality vendors to work with that further ensure a competitive advantage for the company.
Regardless of whether you’re establishing a new procurement process or reevaluating your existing procurement lifecycle steps, the first step towards gaining momentum within the procurement realm is understanding the 17 steps to an efficient procurement cycle and their significance.
To gain a better understanding of the procurement process flowchart, it is imperative to deduce the 17 stages of the procurement cycle.
Procurement cycle
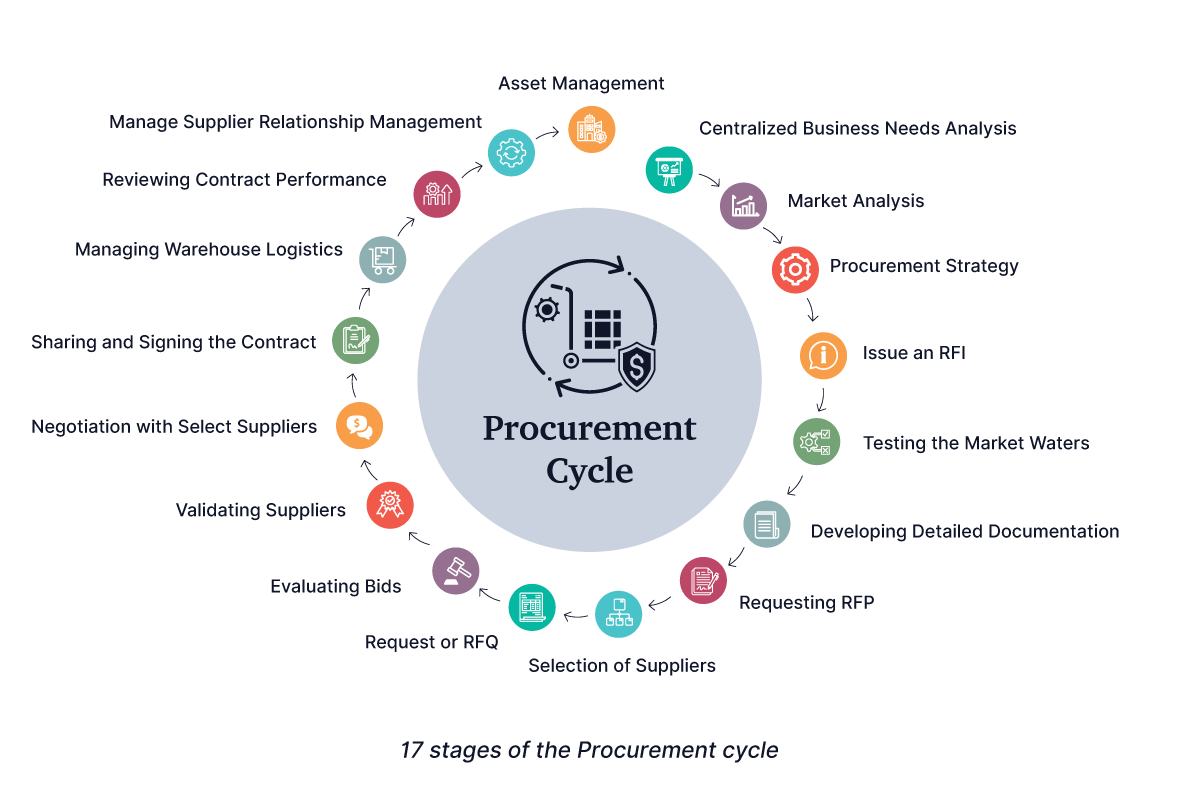
Here’s a detailed account of the 17 stages of the procurement cycle that will help in structuring the process:
1. Conducting a centralized business needs analysis: The first step in the procurement lifecycle is identifying what products need to be procured for your business, when, and why. It is not restricted to a department or business unit. All stakeholders across the entire organization participate in this step and define their respective business needs so that the procurement teams get absolute visibility into who needs what. During the defining stage, procurement teams must also outline product specifications to gain visibility into the spending areas and categories that can highlight cost savings.
2. Conducting market analysis: Once you’ve identified product needs, it is crucial to conduct a thorough market analysis. This step in the procurement process enables you to gather critical information about the availability of your product, quality, price, and suitability of potential suppliers and solutions to make an informed decision. Sometimes, your organization may manufacture the product in-house if procurement from a third-party supplier exceeds its budget limit.
3. Strategizing the procurement: Developing a procurement strategy aligned with your organization’s procurement goal, policy, and processes is imperative for cost optimization. By comprehending market conditions, trends, opportunities, challenges, and the benefits your suppliers will gain from a business association with your company, you can leverage the information to plan negotiations that result in potential cost savings.
4. Issue an RFI: After gathering comprehensive information, the procurement teams issue an RFI (request for information), and invite potential suppliers to share critical information that can help determine their suitability. The RFI asks the prospective vendors to submit details about the business to stay informed about the possible solutions in the market.
5. Testing the market waters: A secret weapon in the procurement cycle is market testing. This pre-tender activity allows procurement teams to undertake soft market testing to gain a detailed and sound understanding of some of the best sources available in the market. Armed with the latest industry insight, this step helps to create healthy competition during the procurement process before committing to a particular tender. Allocating a fixed budget for market testing helps understand market dynamics better.
6. Developing detailed documentation: Before shortlisting suppliers, you must create detailed documentation on the items you intend to purchase. Your market analysis will have already provided you with the exact details of your business’s needs to develop precise specifications for external suppliers. Such information is also critical to suppliers because it helps them give mutually beneficial quotations later.
7. Requesting RFP Documents: Basis the procurement strategy developed in the previous steps and the documentation gathered, the procurement team Requests for Proposal (RFP). Vendors have to submit a comprehensive proposal that includes price offers, quality of the products, flexibility to adapt based on the company’s needs, adherence to the delivery timeline, reliability, risk management of the supplier, and everything in between. It also includes factors that range beyond price such as an elaborate technical proposal.
8. Selection of suppliers: This vital step involves selecting specific suppliers who will later present their bids for the business. A selection is made based on the RFP. Identifying and evaluating suitable suppliers and effectively managing them sets the foundation for a long-term partnership and significantly contributes to the success of a business.
9. Request for RFQ: This step in the procurement process includes an Invitation to Tender (ITT) and a Request for Quotation (RFQ) from shortlisted suppliers. Having as much detailed documentation as possible regarding the business requirements and clear timelines to respond is advisable.
10. Evaluating bids: Once the suppliers have submitted their bids, the procurement team must examine and compare bids that offer the best value. Some businesses have an evaluation team with assigned roles and responsibilities that review and verify with fairness the compliance and eligibility of the bids or proposals submitted.
11. Validating suppliers: Along with the bids, procurement teams validate suppliers proposing their bids to ensure they are legitimate and dependable. This step is important in the procurement process as it not only eliminates any risk associated with dubious suppliers but also strengthens long-term relations with those who are credible.
12. Negotiation with select suppliers: After evaluating the bids, negotiations on the price take place to derive maximum value from the suppliers. This step when done skillfully can achieve cost reductions, optimize budget allocations, and build long-term supplier relations for the company.
13. Sharing and signing the contract: Once the negotiating team and supplier reach acceptable terms, they strike a deal and share official contracts. The contract must communicate requirements and set expectations based on supply dynamics, logistics, invoicing, and other KPIs before being signed by both parties upon agreement.
14. Managing warehouse logistics: Once both parties sign the contract, the procurement team raises a Purchase order (PO) that specifically defines the price, product specifications, and all terms and conditions of the product and service being supplied. Multiple warehouse logistics — including carriers, delivery speed, and frequency of delivery, amongst others are determined and standardized based on product specifications. Thereby, enabling transparency across the procurement process.
15. Reviewing contract performance: No supplier contract is permanent or binding. Hence, companies must periodically monitor, review, and evaluate supplier performance to meet contract terms. Such evaluation helps identify consistency, bottlenecks, or lapses in agreement so that procurement teams can adjust their strategy and tactics to maintain performance efficacy. Procurement teams also use this step to prevent monopolization and explore new suppliers.
16. Ensuring supplier relationship management: Procurement is a continuous process that enables companies to establish and maintain supplier associations throughout the procurement lifecycle process. There should be access to open communication channels to ensure better collaboration, as suppliers willing to work and grow with the organization can accelerate business.
17. Enhancing asset management: Procurement needs may evolve as you scale your business and expand its reach. You must develop an adaptable procurement strategy based on any updated business goals. As procurement management is integral to asset management, it can actively help you support your business goals.
Hope the insights into the individual stages of the procurement process cycle have helped me understand the procurement cycle better. If appropriately applied without any shortcuts, it can magnify the effectiveness of a company’s operations and help bring down overall costs.
Is the procurement cycle the same for all businesses?
While the type of procurement changes based on company needs and industry, but the process outlined above is often the foundation of any procurement cycle.
How software is making the Procurement Lifecycle better?
In the current business landscape, machine learning and artificial intelligence are powerful tools that can significantly impact your organization’s procurement process. Integrating these technologies into the procurement cycle steps can lead to improved collaboration, streamlined transactions, and increased efficiency.
All-in-one procurement software is an ideal solution that can take care of everything from source to payment, providing comprehensive solutions for both direct and indirect procurement needs. It helps eliminate unnecessary manual work and delays that complicate the procurement process cycle. While cost optimization is the primary objective of procurement strategy development, procurement software can help businesses consider various other aspects, ultimately leading to a robust procurement strategy that adds value to the company.
Here’s how having procurement management software enables the optimization of the procurement lifecycle process:
Streamlined process:
Procurement software is designed to automate and streamline various procurement lifecycle steps, such as sourcing, supplier selection, contract and vendor management, invoicing, and everything in between. It automates many of the manual and time-consuming routine transactions associated with data entry, negotiation, invoice processing, and purchase order creation. This makes the procurement process cycle more efficient, allowing procurement professionals to focus more on strategic activities. It also helps to minimize significant errors and delays in the different stages of the procurement process.
Complete visibility of inventory:
Achieving complete visibility of inventory is crucial for optimizing supply chain operations. Procurement software provides the necessary tools to track and manage inventory levels in real time, ultimately helping to control and save indirect costs. This results in increased return on investment (ROI) and reduced total cost of ownership (TCO).
Easy collaboration and approvals:
With dispersed teams across departments and vendors functioning from around the world, procurement software centralizes procurement communication to maximize effective collaboration. It promotes company-wide collaboration by unifying business needs and maximizing efficiency, visibility, and cost management throughout the procurement cycle. It simplifies the request and approval process, facilitating swift action. It also allows buyers to collaborate with suppliers and enables real-time discussions throughout the purchasing process to foster efficient workflow, cutting down the lead time, and reducing the probability of any disruption.
Lesser risk, better strategies with data-backed reporting:
By automating the arduous task of manual report generation, a process prone to error and inefficiency, procurement software gives procurement teams insights into their supply chain processes, vendor performance, and expenditure patterns to create accurate, real-time reports effortlessly, thereby ensuring data-driven decisions. Analytics also help identify cost-saving opportunities that might otherwise go unnoticed. By analyzing historical spending patterns, discount probability, and supplier performance, businesses can enhance strategies, negotiate better deals, and optimize their procurement lifecycle processes for maximum cost efficiency.
Improved Supplier Management:
Automating supplier management with an online platform improves procurement efficiency, promotes a robust supply chain, and enhances operational agility. Benefits of using an online supplier management platform include connecting and collaborating with global suppliers at no extra cost, accessing already registered suppliers, and managing data and performance metrics online to anticipate and avoid disruptions.
Conclusion
In summary, by understanding and appropriately acknowledging all stages of the procurement cycle within the supply chain, taking a collaborative approach to stakeholder relationships, and educating the business about the procurement process’s strategic value, a business can achieve significant transparency and cost-effectiveness throughout the procurement lifecycle.
Get a Free Demo
We'd love to hear from you. Please fill out this form to schedule a demo with us. You can also give a call on +91 76666 82222




